The evolution of girls’ rights has been a journey of significant advancements and persistent challenges. Over the centuries, the rights of girls have been grossly overlooked, leading to a deeply entrenched culture of gender-based discrimination and violence. However, in the face of these challenges, remarkable progress has been made in the realm of girls’ rights globally. Governments, non-governmental organizations, and community groups have rallied together to create policies, implement programs, and challenge social norms that hinder the growth and development of girls. This article aims to explore the changes and impacts on girls’ rights up to today, even in less known locations.
Historical Context of Girls’ Rights
The historical context of girls’ rights is rooted in a past where women and girls were relegated to the background. For centuries, societies worldwide have been patriarchal, meaning that men held most of the power and women were often treated as second-class citizens. This deeply entrenched belief system impacted every facet of a girl’s life, from access to education to participation in public life. In many parts of the world, girls were expected to take on domestic roles and were often denied the same opportunities as boys. Additionally, harmful practices such as child marriage and female genital mutilation were widespread, perpetuating the cycle of abuse and discrimination.
The Global Movement for Girls’ Rights
The global movement for girls’ rights has been instrumental in driving change and creating a more equal world. Several international conventions and treaties have been established to protect the rights of girls, such as the Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC), and the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW). These conventions have been ratified by many countries, which means they have legally agreed to adhere to the principles outlined in these documents. Moreover, global campaigns like ‘HeForShe’ initiated by UN Women, and ‘Because I am a Girl’ by Plan International, have been pivotal in raising awareness and mobilizing support for girls’ rights.
Changes and Impacts

Significant changes have been observed over the years in various aspects of girls’ lives:
- Education: There has been a significant increase in girls’ enrollment in schools worldwide. Efforts to bridge the gender gap in education have led to more girls receiving formal education, and in some regions, girls have even surpassed boys in educational attainment.
- Child Marriage: Many countries have increased the legal age of marriage and are implementing programs to prevent child marriage. Although the practice still persists in some regions, there is a global trend towards its reduction.
- Health: Efforts have been made to improve girls’ health, including increased access to sexual and reproductive health services and efforts to combat female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C).
- Political Participation: More girls and young women are being encouraged to participate in political processes, leading to an increase in the number of female leaders and decision-makers.
Challenges and Ongoing Struggles
Despite the significant progress made, girls continue to face numerous challenges:
- Violence: Girls are still at a high risk of experiencing various forms of violence, including domestic violence, sexual assault, and human trafficking.
- Poverty: Girls are disproportionately affected by poverty, which hampers their access to education, health services, and other essential resources.
- Cultural Norms: Harmful cultural norms and practices, such as son preference, continue to undermine the value of girls and hinder their development.
The Role of Technology
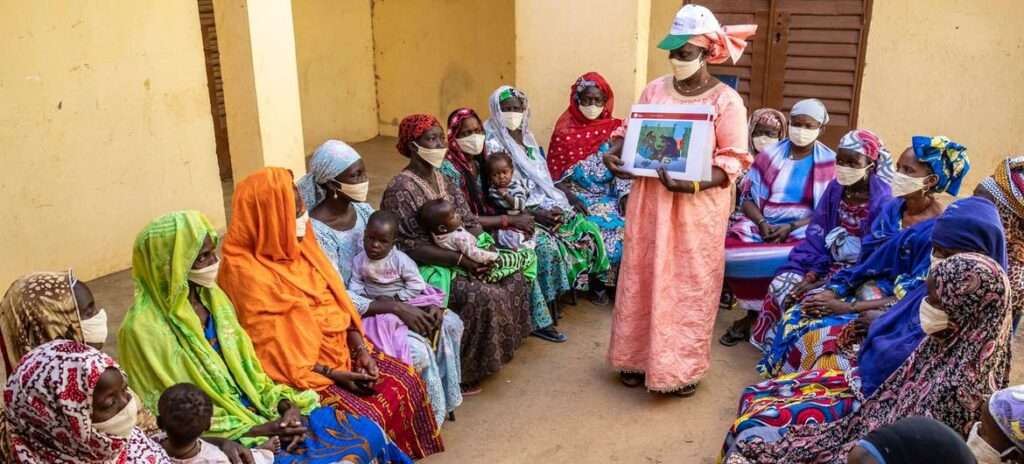

Technology has played a crucial role in advancing girls’ rights. It has provided a platform for girls to connect, share their stories, and mobilize support. Moreover, technological innovations have made it easier to access education and health services, even in remote and less known locations. However, it is essential to address the digital divide that exists, as many girls, particularly in low-income countries, still do not have access to digital devices or the internet.
Conclusion
The journey towards achieving full equality for girls has been marked by significant advancements and persistent challenges. While progress has been made in areas such as education, child marriage prevention, and political participation, girls still face considerable barriers related to violence, poverty, and harmful cultural norms. Technology has emerged as a powerful tool in advancing girls’ rights, but efforts must be made to ensure that all girls, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status, can access and benefit from these technological advancements. Ultimately, the realization of girls’ rights requires a sustained and collective effort from governments, civil society, and communities worldwide.